Medical screenings involve tests or exams performed to detect diseases or health conditions before symptoms appear. They aim to identify problems early when they’re easier to treat or manage. These screenings can include checking blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and conducting cancer screenings like mammograms or colonoscopies. They are crucial because they help catch health issues before they become serious, potentially saving lives and reducing healthcare costs.
Preventive healthcare, which includes regular medical screenings, focuses on maintaining health and preventing diseases rather than just treating them after they occur. It emphasizes healthy habits, such as exercise, balanced nutrition, and avoiding harmful substances. By investing in preventive healthcare, individuals can take charge of their well-being and enjoy a better quality of life.
Table of Contents
What Are Medical Screenings?
Medical screenings are tests or examinations performed to detect potential health problems or diseases in individuals who may not have any symptoms. These screenings are typically conducted as part of preventive healthcare to identify conditions early, when they are more treatable or manageable. Medical screenings can vary widely depending on factors such as age, gender, and medical history. They may involve physical exams, laboratory tests, imaging studies (like X-rays or MRIs), or other specialized procedures.
The purpose of medical screenings is to assess a person’s risk for certain diseases or conditions and to provide opportunities for early intervention or preventive measures. Examples of common medical screenings include blood pressure checks, cholesterol screenings, mammograms for breast cancer, and colonoscopies for colorectal cancer. These screenings play a crucial role in promoting good health by enabling healthcare providers to identify and address potential health issues before they become more serious or symptomatic.
Role of Medical Screenings in Preventive Healthcare
Medical screenings play a pivotal role in preventive healthcare by enabling early detection of potential health issues, thus facilitating timely interventions to prevent the development or progression of diseases. These screenings are essential for identifying risk factors and detecting abnormalities before symptoms manifest, allowing healthcare providers to implement appropriate measures to mitigate or manage these risks effectively.
By conducting regular screenings, individuals can actively monitor their health status and identify any deviations from normal ranges. This proactive approach empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their health and lifestyle choices, such as adopting healthier dietary habits, engaging in regular physical activity, or quitting smoking, to reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases.
Moreover, medical screenings contribute to reducing healthcare costs by averting the need for expensive treatments or hospitalizations that may result from untreated or undiagnosed conditions. Ultimately, the role of medical screenings in preventive healthcare is paramount, as they serve as a cornerstone for promoting wellness, enhancing longevity, and fostering a culture of proactive health management within communities.
Common Medical Screenings
Common medical screenings encompass a range of tests and examinations aimed at detecting various health conditions or diseases early, often before symptoms develop.
Blood Pressure Screening
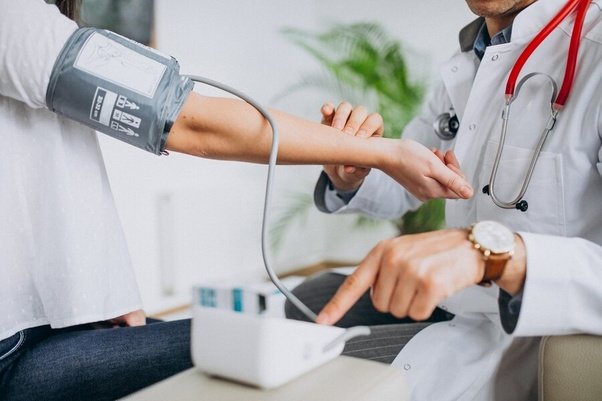
High blood pressure, or hypertension, often has no symptoms but can lead to serious health issues like heart disease and stroke if left untreated. Screening for blood pressure is typically a quick and non-invasive procedure done using a blood pressure cuff around the arm.
It’s recommended that adults have their blood pressure checked at least once a year, or more frequently if they have risk factors such as obesity or a family history of hypertension. Early detection through regular screenings allows for lifestyle modifications or medication management to control blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications.
Cholesterol Screening
High levels of cholesterol in the blood can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Cholesterol screenings typically involve a blood test to measure levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol, HDL (good) cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Screening is especially important for individuals with a family history of heart disease, diabetes, or obesity. Results from cholesterol screenings help healthcare providers determine the need for lifestyle changes, medication, or further diagnostic tests.
Blood Glucose Testing
Screening for blood glucose levels is crucial for detecting diabetes or prediabetes, conditions that can lead to serious complications if not managed properly. Tests may include fasting blood sugar tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, or A1C tests, depending on individual risk factors and symptoms.
Early detection allows for timely intervention through dietary changes, exercise, medication, or insulin therapy to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Regular monitoring is especially important for individuals with risk factors such as obesity, family history of diabetes, or sedentary lifestyle.
Cancer Screenings
Cancer screenings aim to detect various types of cancer at early stages when treatment is most effective. Mammograms are recommended for women starting at age 40 to screen for breast cancer, and Pap smears are advised for cervical cancer screening starting at age 21.
Colonoscopies are crucial for detecting colorectal cancer and are typically recommended starting at age 50 for average-risk individuals. Early detection through screenings can significantly improve cancer outcomes and increase chances of successful treatment and survival.
Benefits and Challenges of Medical Screenings
Benefits of Medical Screenings
- Early Detection of Diseases: Medical screenings can identify health issues in their early stages, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment, which can improve outcomes and reduce the severity of conditions.
- Preventive Care: Regular screenings enable individuals to take proactive steps to maintain their health and prevent the development or progression of diseases by adopting healthy lifestyle choices and interventions.
- Improved Health Outcomes: Early detection and treatment resulting from screenings can lead to better health outcomes, reduced morbidity, and mortality rates associated with various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Despite initial costs, medical screenings can be cost-effective in the long run by averting the need for more expensive treatments, hospitalizations, or surgeries that may result from untreated or advanced diseases.
- Empowerment and Peace of Mind: Knowing one’s health status through screenings can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health, leading to a sense of control and peace of mind.
Challenges of Medical Screenings
- False Positives and Overdiagnosis: Some screening tests may yield false-positive results, leading to unnecessary follow-up tests, anxiety, and potential harm from overdiagnosis and overtreatment.
- False Negatives: Conversely, false-negative results may occur, providing individuals with a false sense of security and delaying necessary treatment or intervention.
- Risk of Complications: Invasive screening procedures, such as colonoscopies or biopsies, carry risks of complications such as bleeding or infection, although these risks are typically low.
- Adherence and Access: Limited access to healthcare services, lack of awareness, and barriers such as cost or transportation may hinder individuals from undergoing recommended screenings, particularly in underserved populations.
- Ethical Considerations: There are ethical considerations regarding the balance between benefits and harms of screenings, as well as issues related to informed consent, equity, and resource allocation within healthcare systems.
Promoting Access to Medical Screenings
Promoting access to medical screenings is essential for ensuring that individuals have the opportunity to benefit from early detection and preventive healthcare measures.
Community Outreach Programs
Establishing community-based initiatives that bring screenings to underserved areas can help overcome barriers such as transportation issues and lack of awareness. Mobile clinics, community health fairs, and partnerships with local organizations can increase access to screenings.
Reducing Financial Barriers
Implementing policies to provide free or low-cost screenings, particularly for high-risk populations or those with limited financial resources, can make screenings more accessible. This may involve expanding insurance coverage, subsidizing screening costs, or offering sliding-scale fees based on income.
Patient Education and Empowerment
Increasing health literacy and awareness about the importance of screenings through educational campaigns can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards their health. This includes providing information about recommended screenings based on age, gender, and risk factors, as well as addressing myths or misconceptions that may deter people from seeking screenings.
Telemedicine and Remote Screening Options
Leveraging technology to offer telemedicine consultations and remote screening options can expand access to screenings, particularly for individuals in rural or remote areas with limited access to healthcare facilities. Telehealth platforms can provide convenient and timely access to healthcare providers for consultations and referrals for screenings.
Cultural Competence and Linguistic Accessibility
Ensuring that screening programs are culturally competent and linguistically accessible is crucial for reaching diverse populations. Providing materials in multiple languages, offering interpretation services, and tailoring outreach efforts to the specific needs and preferences of different communities can help increase participation in screenings.
Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
Collaborating with healthcare providers and clinics to integrate screening services into routine care can streamline the process and encourage uptake. This includes incorporating reminders for screenings during primary care visits, implementing electronic health record systems to track screening recommendations, and facilitating referrals for screenings as part of comprehensive care plans.
Conclusion
Medical screenings play a vital role in promoting good health by detecting potential health issues early before they become serious. These screenings, ranging from blood pressure checks to cancer screenings, provide opportunities for early intervention and treatment, ultimately improving health outcomes and quality of life.
By participating in regular medical screenings, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining their health and well-being. Early detection allows for timely interventions, such as lifestyle modifications, medication management, or preventive measures, to address health concerns and reduce the risk of complications.